publications
2025
- Preprint
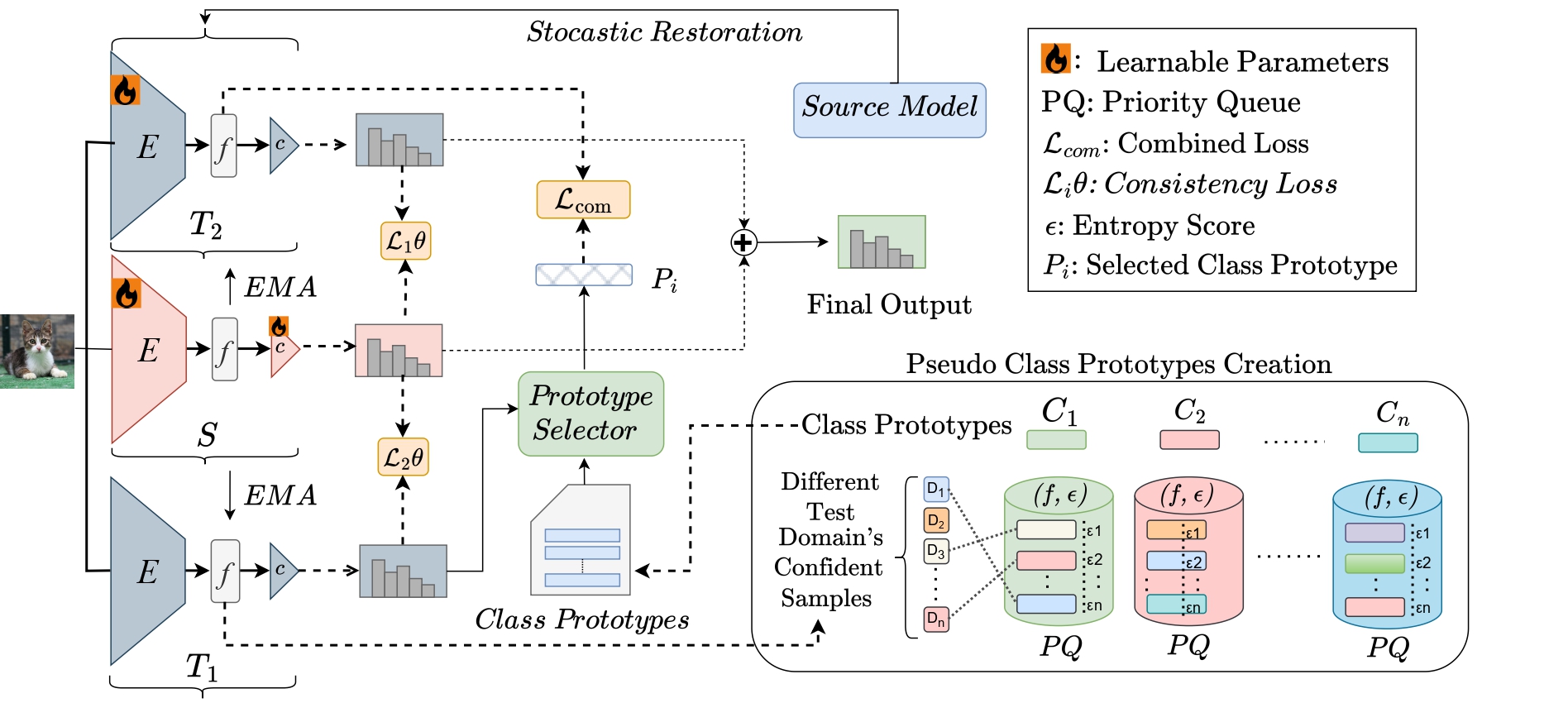 SloMo-Fast: Slow-Momentum and Fast-Adaptive Teachers for Source-Free Continual Test-Time Adaptation2025
SloMo-Fast: Slow-Momentum and Fast-Adaptive Teachers for Source-Free Continual Test-Time Adaptation2025Continual Test-Time Adaptation (CTTA) is crucial for deploying models in real-world applications with unseen, evolving target domains. Existing CTTA methods, however, often rely on source data or prototypes, limiting their applicability in privacy-sensitive and resource-constrained settings. Additionally, these methods suffer from long-term forgetting, which degrades performance on previously encountered domains as target domains shift. To address these challenges, we propose SloMo-Fast, a source-free, dual-teacher CTTA framework designed for enhanced adaptability and generalization. It includes two complementary teachers: the Slow-Teacher, which exhibits slow forgetting and retains long-term knowledge of previously encountered domains to ensure robust generalization, and the Fast-Teacher rapidly adapts to new domains while accumulating and integrating knowledge across them. This framework efficiently preserves knowledge of past domains, adapts efficiently to new ones. Our extensive experimental results demonstrate that SloMo-Fast consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across CTTA benchmarks, achieving a mean error rate of 33.8% in various TTA settings. Notably, it surpasses existing methods by a margin of at least 1.5%. Additionally, SloMo-Fast achieves significant performance improvements in Mixed Domain and our proposed new benchmark Mixed domain comes after Continual Domain scenarios along with Cyclic repeatation in continual test time adaptation setting, indicating its ability to learn generalized representations across domains.
- Preprint
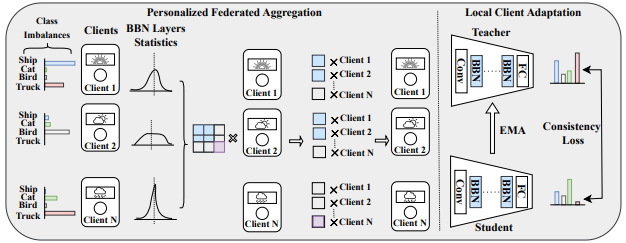 pFedBBN: A Personalized Federated Test-Time Adaptation with Balanced Batch Normalization for Class-Imbalanced Data2025
pFedBBN: A Personalized Federated Test-Time Adaptation with Balanced Batch Normalization for Class-Imbalanced Data2025Federated learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across decentralized clients while preserving the privacy of local data. Class imbalance remains a fundamental challenge in FL, where rare but critical classes are often severely underrepresented in individual client datasets. Although prior work has addressed class imbalance during training through reliable aggregation and local class distribution alignment, these methods typically rely on access to labeled data or coordination among clients, and none are designed for unsupervised adaptation during inference under federated constraints. We propose a new approach called pFedBBN, a personalized federated test-time adaptation framework that incorporates balanced batch normalization (BBN) to mitigate prediction bias by treating all classes equally during feature normalization, while also enabling a weighted collaboration of clients based on their BBN statistics, which indicates that clients from similar domains prioritize each other more during adaptation. The method supports fully unsupervised local adaptation and introduces a class-aware model aggregation strategy that enables personalized inference without compromising privacy. It effectively addresses both distribution shifts and class imbalance through balanced feature normalization and domain-aware collaboration, without requiring any labeled or raw data from clients. Experiments on corrupted versions of CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 demonstrate that pFedBBN significantly improves robustness and performance on minority classes compared to existing federated and test-time adaptation baselines.
- Accepted
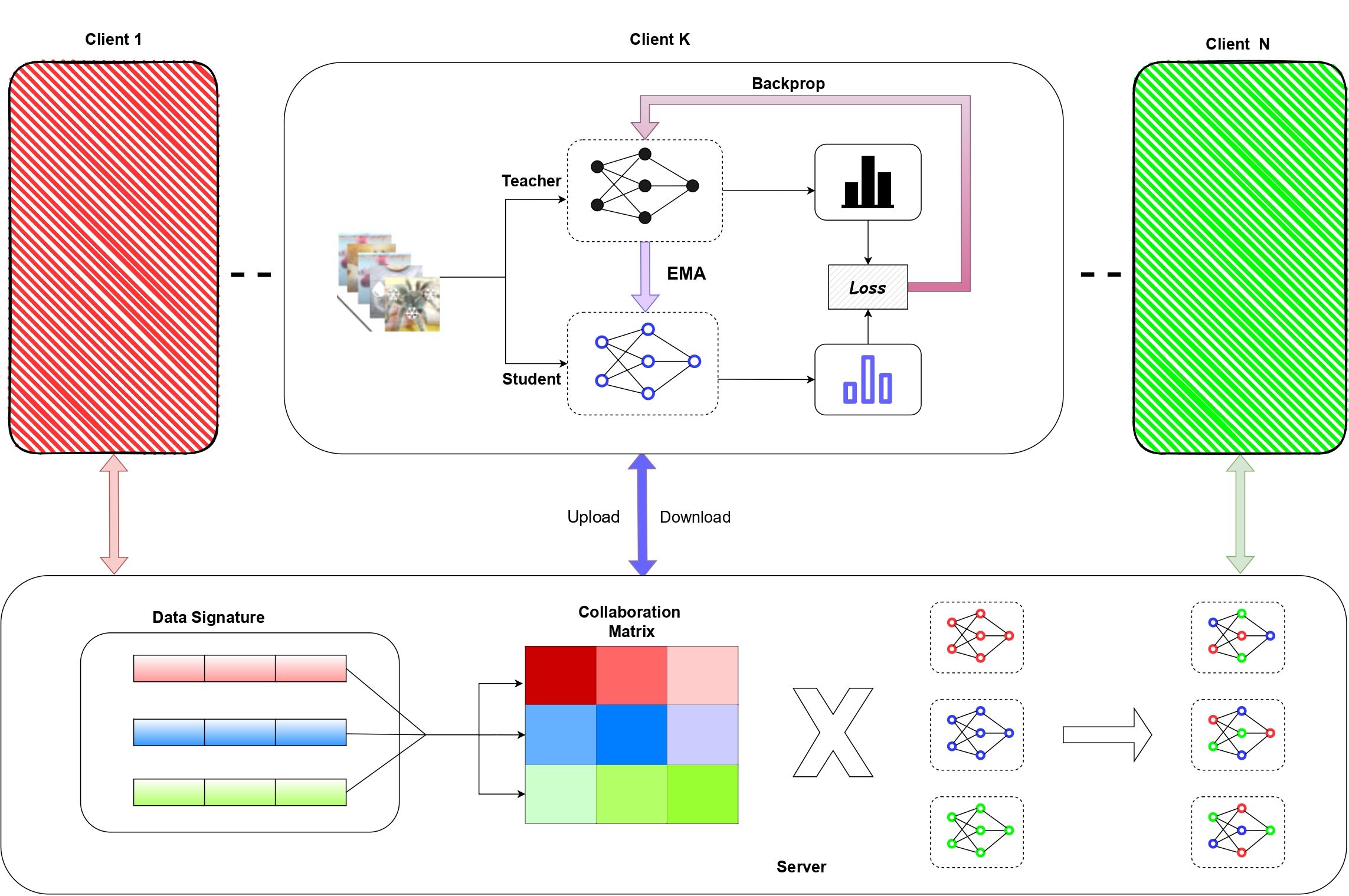 FedCTTA: A Collaborative Approach to Continual Test-Time Adaptation in Federated LearningIn 2025 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN-2025), 2025
FedCTTA: A Collaborative Approach to Continual Test-Time Adaptation in Federated LearningIn 2025 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN-2025), 2025Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across distributed clients without sharing raw data, making it ideal for privacy-sensitive applications. However, FL models often suffer performance degradation due to distribution shifts between training and deployment. Test-Time Adaptation (TTA) offers a promising solution by allowing models to adapt using only test samples. However, existing TTA methods in FL face challenges such as computational overhead, privacy risks from feature sharing, and scalability concerns due to memory constraints. To address these limitations, we propose Federated Continual Test-Time Adaptation (FedCTTA), a privacy-preserving and computationally efficient framework for federated adaptation. Unlike prior methods that rely on sharing local feature statistics, FedCTTA avoids direct feature exchange by leveraging similarity-aware aggregation based on model output distributions over randomly generated noise samples. This approach ensures adaptive knowledge sharing while preserving data privacy. Furthermore, FedCTTA minimizes the entropy at each client for continual adaptation, enhancing the model’s confidence in evolving target distributions. Our method eliminates the need for server-side training during adaptation and maintains a constant memory footprint, making it scalable even as the number of clients or training rounds increases. Extensive experiments show that FedCTTA surpasses existing methods across diverse temporal and spatial heterogeneity scenarios.
- Accepted
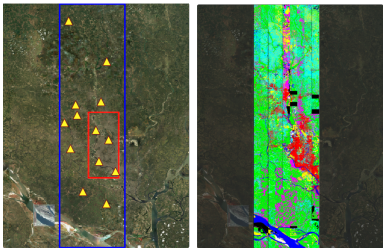 BD Open LULC Map: High-Resolution Land Use and Land Cover Mapping & Benchmarking for Urban Development in Dhaka, BangladeshMir Sazzat Hossain, Ovi Paul, Md Akil Raihan Iftee, and 7 more authorsIn 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2025
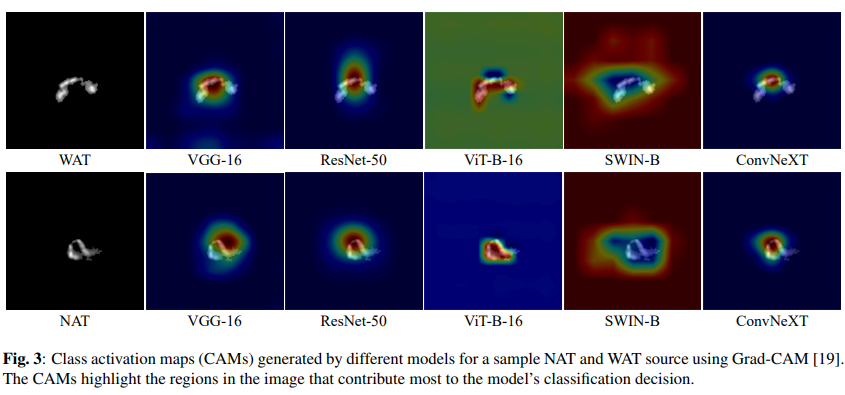
BD Open LULC Map: High-Resolution Land Use and Land Cover Mapping & Benchmarking for Urban Development in Dhaka, BangladeshMir Sazzat Hossain, Ovi Paul, Md Akil Raihan Iftee, and 7 more authorsIn 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2025We introduce a novel machine learning dataset tailored for the classification of bent radio active galactic nuclei (AGN) in astronomical observations. Bent radio AGN, distinguished by their curved jet structures, provide critical insights into galaxy cluster dynamics, interactions within the intracluster medium, and the broader physics of AGN. Despite their astrophysical significance, the classification of bent AGN remains a challenge due to the scarcity of specialized datasets and benchmarks. To address this, we present a dataset derived from a well recognized radio astronomy survey, designed to support the classification of NAT (Narrow-Angle Tail) and WAT (Wide-Angle Tail) categories, along with detailed data processing steps. We further evaluate the performance of stateof-the-art deep learning models on the dataset, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and transformer-based architectures. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of advanced machine learning models in classifying bent radio AGN, with ConvNeXT achieving the highest F1-scores for both NAT and WAT sources. By sharing this dataset and benchmarks, we aim to facilitate the advancement of research in bent AGN classification, AGN and cluster environments, galaxy evolution, and more.
- Accepted
 RGC-BENT: A NOVEL DATASET FOR BENT RADIO GALAXY CLASSIFICATIONM.S. Hossain, K.M.B. Asad, P. Saikia, and 7 more authorsIn 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2025
RGC-BENT: A NOVEL DATASET FOR BENT RADIO GALAXY CLASSIFICATIONM.S. Hossain, K.M.B. Asad, P. Saikia, and 7 more authorsIn 2025 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2025We introduce a novel machine learning dataset tailored for the classification of bent radio active galactic nuclei (AGN) in astronomical observations. Bent radio AGN, distinguished by their curved jet structures, provide critical insights into galaxy cluster dynamics, interactions within the intracluster medium, and the broader physics of AGN. Despite their astrophysical significance, the classification of bent AGN remains a challenge due to the scarcity of specialized datasets and benchmarks. To address this, we present a dataset derived from a well recognized radio astronomy survey, designed to support the classification of NAT (Narrow-Angle Tail) and WAT (Wide-Angle Tail) categories, along with detailed data processing steps. We further evaluate the performance of stateof-the-art deep learning models on the dataset, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and transformer-based architectures. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of advanced machine learning models in classifying bent radio AGN, with ConvNeXT achieving the highest F1-scores for both NAT and WAT sources. By sharing this dataset and benchmarks, we aim to facilitate the advancement of research in bent AGN classification, AGN and cluster environments, galaxy evolution, and more.
2024
- Published
 MoE-TTA: Enhancing Continual Test-Time Adaptation for Vision-Language Models through Mixture of ExpertsMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Wahida Mahjabin, Anik Ekka, and 1 more authorIn 2024 27th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), 2024
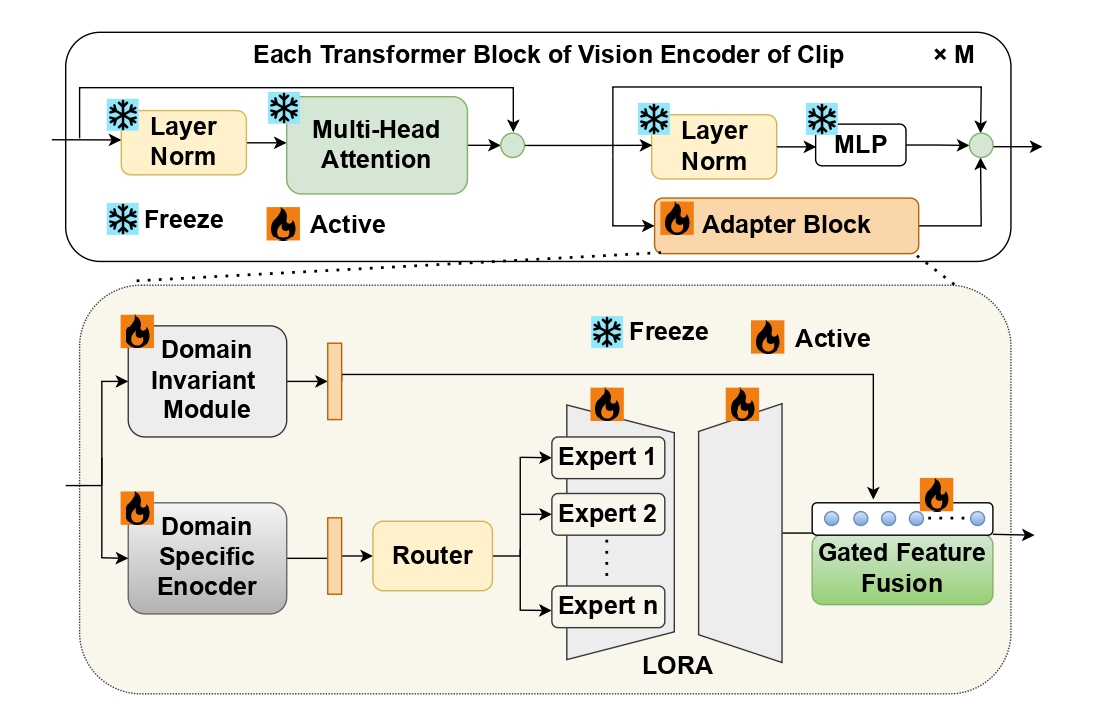
MoE-TTA: Enhancing Continual Test-Time Adaptation for Vision-Language Models through Mixture of ExpertsMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Wahida Mahjabin, Anik Ekka, and 1 more authorIn 2024 27th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), 2024Continual learning enables vision-language models to incrementally acquire new knowledge without relying on access to the entire historical dataset. This capability is crucial for adapting to evolving data distributions in real-world scenar- ios, where models must handle domain shifts and incorporate new information while retaining previously learned knowledge. However, maintaining performance in large-scale models remains challenging due to parameter shifts during learning and the sig- nificant computational costs associated with full-model updates. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel method for Continual Test-Time Domain Adaptation (CTTDA) on vision- language datasets, leveraging a MoE and adapter modules to optimize domain-specific adaptation while maintaining zero-shot classification capabilities. Utilising LoRA in MoE framework within transformer layers, the model efficiently updates a small set of parameters by dynamically selecting experts. This approach minimizes computational costs by activating only a portion of the model, avoiding the need for full-model updates during domain adaptation. During test-time adaptation, entropy loss is calculated without access to labels, improving the model’s fine-tuning and guiding towards confident predictions across domains. A contrastive warm-up phase further optimizes the adapter blocks by enhancing the differentiation of domain-specific and domain- invariant features, thereby establishing a strong foundation for effective test-time adaptation. The proposed MoE-TTA model achieves an average accuracy of 36.43% across diverse ImageNet datasets and 32.93% in fine-grained classification, demonstrating promising results, especially in datasets like EuroSAT (51.67%), while being lower than several competitors, with no doubt in its ability to capture domain shifts effectively.
- Published
 Organ-Seg: A Vision-Language and LLM-Enhanced Framework for User-Guided Abdominal Organ Image SegmentationMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Tasfia Faija, Partho Choudhury Shoumya, and 1 more authorIn 2024 27th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), 2024
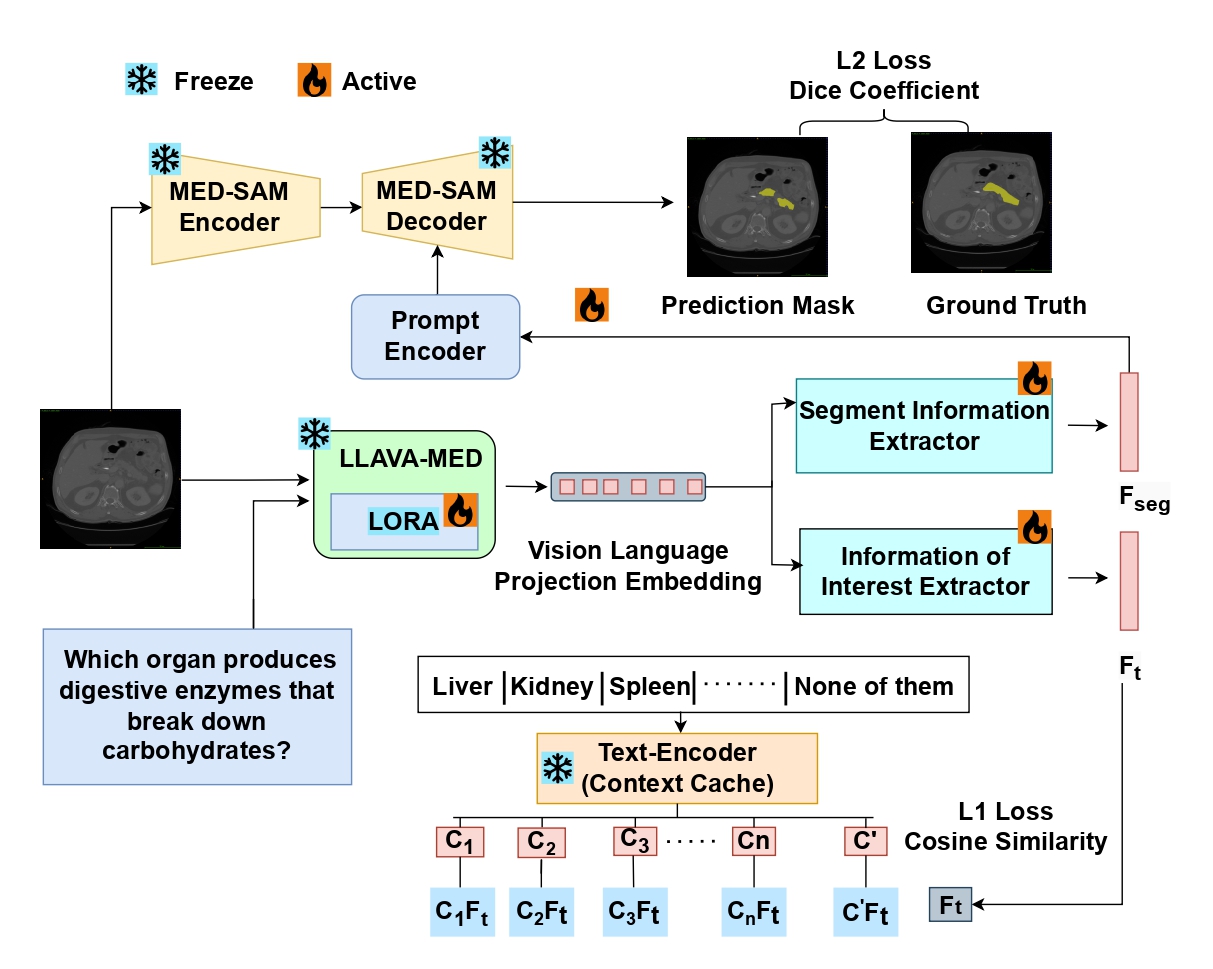
Organ-Seg: A Vision-Language and LLM-Enhanced Framework for User-Guided Abdominal Organ Image SegmentationMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Tasfia Faija, Partho Choudhury Shoumya, and 1 more authorIn 2024 27th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), 2024Medical image segmentation plays a vital role in diagnostic and treatment planning, where precision is crucial for accurate outcomes. Traditional segmentation methods, while effective in many areas, often fail to incorporate user-driven guidance, leading to errors in region identification, especially when irrelevant regions are segmented. In this study, we present a new, instruction-based medical image segmentation framework that enhances user interaction while delivering precise and context-aware results. Our approach addresses the limitations of previous works, such as vision-large language models (LLM) like LLaVA, which provide context but do not perform segmentation, and the Segment Anything Model, which performs segmenta- tion but does not incorporate user’s text-guided instruction. We propose a segmentation model framework that combines vision-language embeddings from LLava with SAM to perform accurate, query-based segmentation of medical images. A key innovation of our model framework is its ability to handle false premises—situations where a user queries for an organ not present in the image—by employing a similarity-based mechanism that prevents incorrect segmentation. Tested on MRI datasets, FLARE22, our system achieves the highest segmentation dice coefficient 63.9%, with significantly improved relevance and reliability. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in refining segmentation quality and enhancing user- guided interaction, thus offering an advanced tool for medical imaging applications.
- Published
 Next-Gen Heart Disease Prediction: A Gradient Boosting Approach with L1-Regularized Neural NetworksMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Raiyan Ashraf, Atiqul Islam, and 2 more authorsIn 2024 27th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), 2024
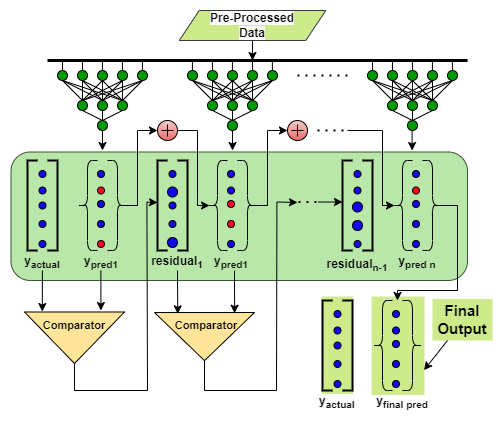
Next-Gen Heart Disease Prediction: A Gradient Boosting Approach with L1-Regularized Neural NetworksMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Raiyan Ashraf, Atiqul Islam, and 2 more authorsIn 2024 27th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), 2024Medical image segmentation plays a vital role in diagnostic and treatment planning, where precision is crucial for accurate outcomes. Traditional segmentation methods, while effective in many areas, often fail to incorporate user-driven guidance, leading to errors in region identification, especially when irrelevant regions are segmented. In this study, we present a new, instruction-based medical image segmentation framework that enhances user interaction while delivering precise and context-aware results. Our approach addresses the limitations of previous works, such as vision-large language models (LLM) like LLaVA, which provide context but do not perform segmentation, and the Segment Anything Model, which performs segmenta- tion but does not incorporate user’s text-guided instruction. We propose a segmentation model framework that combines vision-language embeddings from LLava with SAM to perform accurate, query-based segmentation of medical images. A key innovation of our model framework is its ability to handle false premises—situations where a user queries for an organ not present in the image—by employing a similarity-based mechanism that prevents incorrect segmentation. Tested on MRI datasets, FLARE22, our system achieves the highest segmentation dice coefficient 63.9%, with significantly improved relevance and reliability. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in refining segmentation quality and enhancing user- guided interaction, thus offering an advanced tool for medical imaging applications.
2023
- Thesis Book
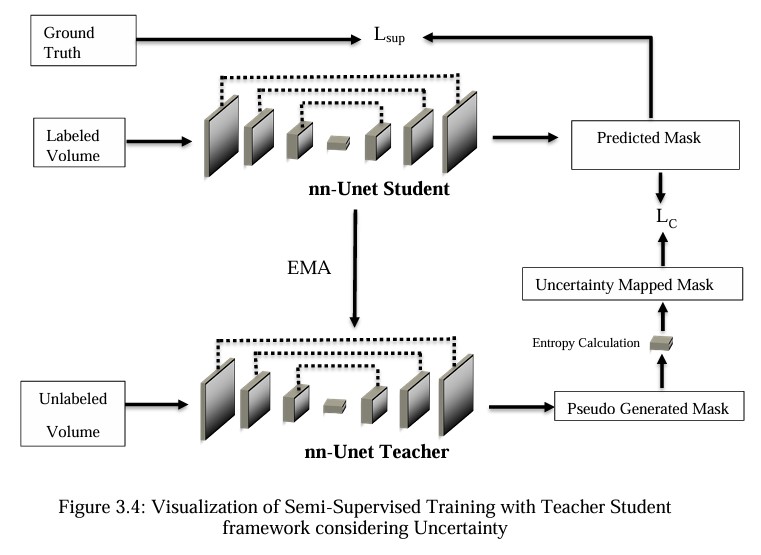 3D Cerebrovascular Segmentation Using Semi-Supervised ApproachSk. Imran Hossain MD Akil Raihan Iftee2023
3D Cerebrovascular Segmentation Using Semi-Supervised ApproachSk. Imran Hossain MD Akil Raihan Iftee2023 - Published
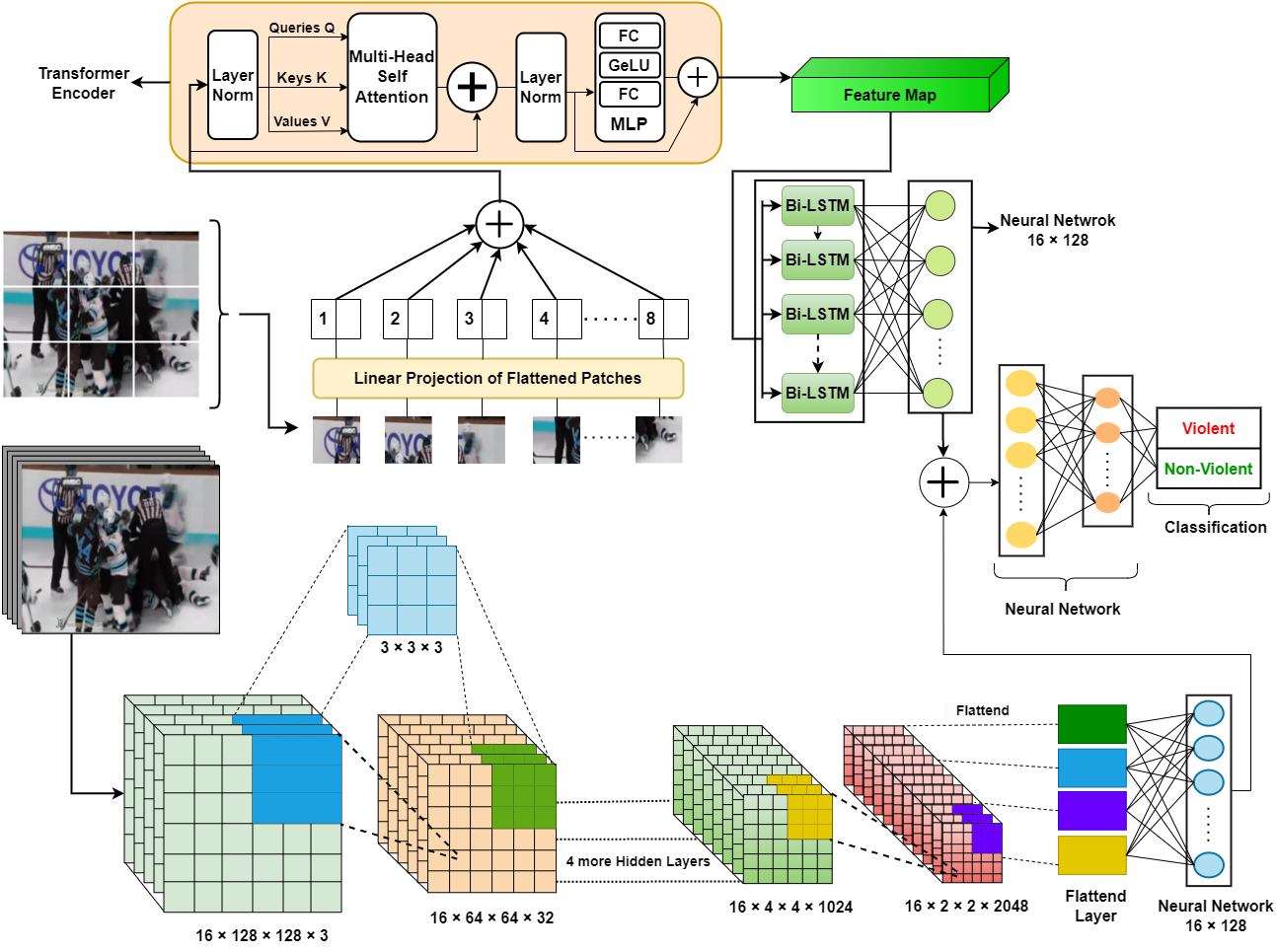 VioNet: An Enhanced Violence Detection Approach for Videos Using a Fusion Model of Vision Transformer with Bi-LSTM and 3D Convolutional Neural NetworksMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Md Mominur Rahman, and Sunanda DasIn International Conference on Big Data, IoT and Machine Learning, 2023
VioNet: An Enhanced Violence Detection Approach for Videos Using a Fusion Model of Vision Transformer with Bi-LSTM and 3D Convolutional Neural NetworksMd Akil Raihan Iftee, Md Mominur Rahman, and Sunanda DasIn International Conference on Big Data, IoT and Machine Learning, 2023The identification of violence in real-world scenarios is imperative as it enables the detection of aggressive behavior, thereby preventing harm to individuals and communities. This is crucial for ensuring public safety and maintaining social order.
- Published
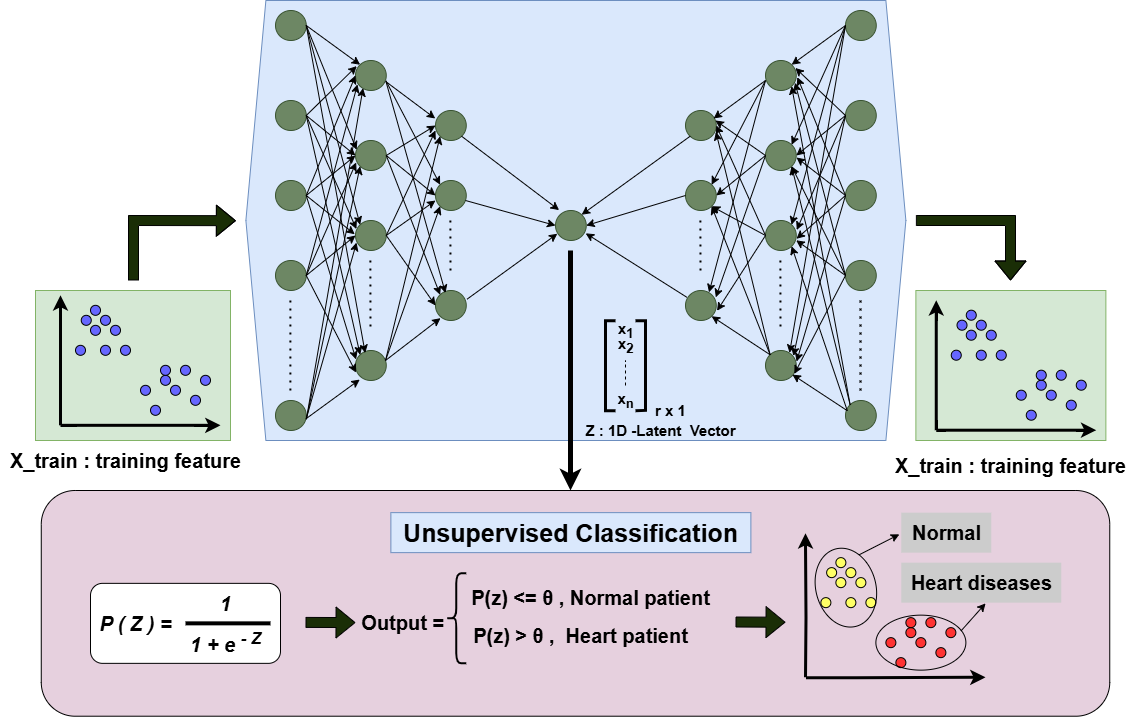 Unsupervised Binary Classification of Heart Diseases Using an Autoencoder Model with Boosting AlgorithmMd Akil Raihan Iftee, and Sunanda DasIn 2023 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), 2023
Unsupervised Binary Classification of Heart Diseases Using an Autoencoder Model with Boosting AlgorithmMd Akil Raihan Iftee, and Sunanda DasIn 2023 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), 2023The identification of violence in real-world scenarios is imperative as it enables the detection of aggressive behavior, thereby preventing harm to individuals and communities. This is crucial for ensuring public safety, facilitating effective crime investigation, promoting child safety, safeguarding mental health, and facilitating social media moderation. Various methods, including handcrafted techniques and deep learning algorithms, can be utilized in surveillance or CCTV cameras, as well as smartphones, to enable timely detection of violent behavior and facilitate appropriate action and intervention. In this study, we introduce VioNET, a novel approach that combines a 3D Convolutional Neural Network and a Vision Transformer with Bidirectional LSTM for the purpose of accurately detecting violence in video data. Since video data is inherently sequential, the extraction of spatiotemporal features is essential to accurate detection. The use of these two deep learning methods facilitates the extraction of maximum features, which are then fused together to classify videos with the highest possible accuracy. We evaluate the effectiveness of our approach by employing three datasets: Hockey, Movies, and Violent Flow, for analysis. The proposed model achieved impressive accuracies of 97.85%, 100.00%, and 96.33% on the Hokey, Movie, and Violent Flow datasets, respectively. Based on the obtained results, it is evident that our method showcases superior performance, outperforming several existing approaches in the field and establishing itself as a robust and competitive solution for violence detection in videos.
2022
- Published
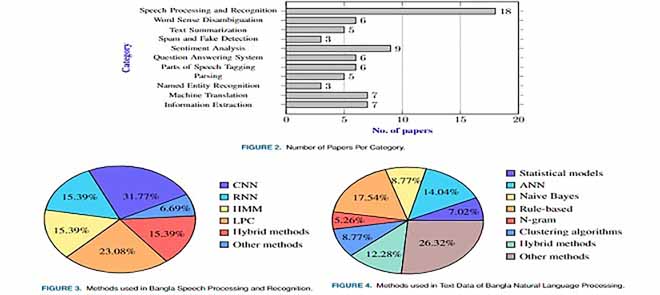 Bangla natural language processing: A comprehensive analysis of classical, machine learning, and deep learning-based methodsOvishake Sen, Mohtasim Fuad, Md Nazrul Islam, and 8 more authorsIEEE Access, 2022
Bangla natural language processing: A comprehensive analysis of classical, machine learning, and deep learning-based methodsOvishake Sen, Mohtasim Fuad, Md Nazrul Islam, and 8 more authorsIEEE Access, 2022The Bangla language is the seventh most spoken language, with 265 million native and non-native speakers worldwide. However, English is the predominant language for online resources and...
2021
- Published
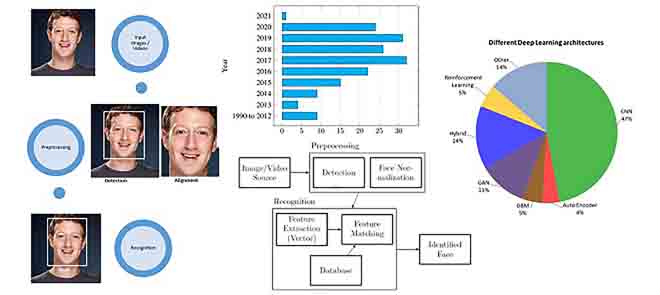 Recent advances in deep learning techniques for face recognitionMd Tahmid Hasan Fuad, Awal Ahmed Fime, Delowar Sikder, and 6 more authorsIEEE Access, 2021
Recent advances in deep learning techniques for face recognitionMd Tahmid Hasan Fuad, Awal Ahmed Fime, Delowar Sikder, and 6 more authorsIEEE Access, 2021In recent years, researchers have proposed many deep learning (DL) methods for various tasks, and particularly face recognition (FR) made an enormous leap using these techniques. Deep FR systems benefit from the hierarchical architecture of the DL methods to learn discriminative face representation. Therefore, DL techniques significantly improve state-of-the-art performance on FR systems and encourage diverse and efficient real-world applications. In this paper, we present a comprehensive analysis of various FR systems that leverage the different types of DL techniques, and for the study, we summarize 171 recent contributions from this area. We discuss the papers related to different algorithms, architectures, loss functions, activation functions, datasets, challenges, improvement ideas, current and future trends of DL-based FR systems. We provide a detailed discussion of various DL methods to understand the current state-of-the-art, and then we discuss various activation and loss functions for the methods. Additionally, we summarize different datasets used widely for FR tasks and discuss challenges related to illumination, expression, pose variations, and occlusion. Finally, we discuss improvement ideas, current and future trends of FR tasks.